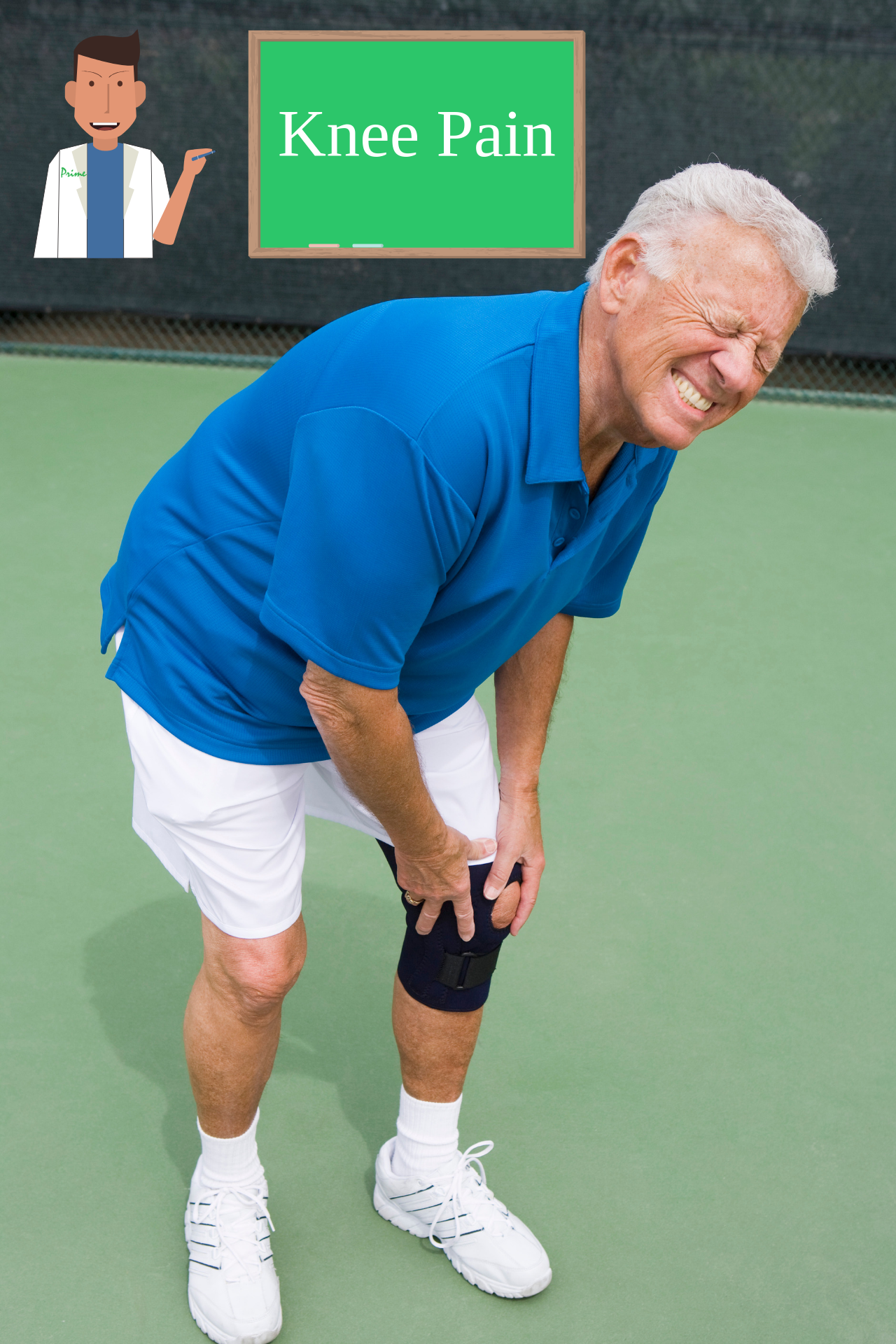
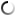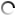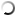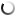Knee pain
This post is also available in: 中文
Get to know the knee joint
The knee joint is the largest and most complicated joint in our body. It is made up of the femur on top, tibia at the bottom, and the patella at the front.
Cause of knee injuries
The knee joint undergoes large stress in turning or sudden stops to absorb shock and stabilize the body. The accomplishment of these functions requires contribution from the joint cartilage, meniscus, ligaments and muscles. Damage to any of these structures can lead to knee pain and functional impairments.
Meniscus injury
Meniscus may split under large torsional stress in turning. Joint stiffness and swelling may occur as well as clicking and locking. The swelling may progress to a chronic stage due to accumulation of fluid inside the joint.
Tendinitis and bursitis
Inflammation of tendon and bursa may develop due to overuse, which often arises from excessive use or inadequate warm-up. The inflamed area is often tender. Serious bursitis may lead to swelling of the whole joint.
Ligament sprain
Trauma, road accident or intensive exercise may lead to ligament sprain or torn. Most commonly affected are the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and medial collateral ligament (MCL). One third of the patients hear a popping sound during the injury. Most ACL tear will lead to hemarthrosis, which is bleeding inside the joint. Pain is experienced deep inside the joint and movements are unstable.
Degenerative arthritis
With the aging process, the muscles in the thigh are not strong enough to support the knee joint, thus speeding up the wear and tear on the cartilage. Over time, the subchondral bone underlying the cartilage is exposed. The subchondral bone is innervated by nerve, while the cartilage is not. With compression directly onto the subchondral bone, the nerves are irritated, thus leading to pain. Besides, degenerative arthritis is often accompanied by synovitis. Acute onset of synovitis gives rise to joint swelling, making walking very difficult.
Muscle imbalance
Trauma, overuse or poor posture can lead to mal-alignment in the lumbar spine or pelvis, leading to increased muscle tension in anterior and inner thigh. The balance of muscle pull on the patella is then disturbed, speeding up degeneration.
Physiotherapy for knee pain
Ice therapy
Ice therapy can be used to decrease pain and swelling.
Electrotherapy
Electrotherapies such as ultrasound and interferential therapy (IFT) can increase blood circulation around the affected joint thus help to decrease pain and inflammation.
Exercise therapy
Exercise is usually used to strengthen the muscles at the front of the thigh as well as to increase flexibility.
Manual therapy
Stiff joints need to be mobilized so as to gain more range of movement. Mal-alignment of the pelvis or lumbar spine need to be corrected so as to reduce the stress on the knee and minimize the referral pain from the spine or pelvis.
Corrective insole
Corrective insole can improve the alignment of the foot, ankle and knee and provide more support, so that overuse can be reduced.
Prevention and maintenance
- When the joint is swollen, walking up or down stairs or slopes should be avoided
- Decrease stress on the knee: avoid squatting, kneeling; overweight patients need to decrease body weight
- Avoid wearing slippers or high heels for long distance walking
- Popping sounds from the joint during movement is a sign of degeneration. Medical advice should be sought if it is accompanied with pain.